Conservation Technology: An Overview
Our world is driven by technology, and conservation technology and nature tech has emerged as a critical tool in the fight to protect our planet's wildlife and natural habitats. This field leverages a variety of innovative tools and systems to address the urgent challenges of conservation in more efficient and effective ways. From the dense jungles to the vast oceans, conservation technology is playing an essential role in ensuring the survival of countless species and ecosystems.
Key Concepts:
- Conservation Technology Defined: Conservation technology encompasses a broad range of software, tools and innovations designed to monitor, protect, and restore wildlife and natural habitats. It leverages advancements in tech to address some of the most pressing environmental challenges.
- Core Technologies: The most significant conservation technologies include camera traps, GIS and remote sensing, environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis, drones, tagging and collaring, acoustic monitoring, AI and machine learning, and mobile apps.
- Challenges in Implementation: Despite the promise of conservation technology, several barriers such as high costs, lack of technical skills, limited access to training, and competition for funding can hinder its widespread adoption.
- Importance of Collaboration: To fully realize the potential of conservation technology, global collaboration, data sharing, capacity building, and investment from governments, philanthropists, and the private sector are crucial.
- Future Potential: The ongoing technological revolution in conservation holds the potential to make conservation efforts more efficient, scalable, and impactful, but it requires an emphasis on user-friendly, purpose-fit solutions.
What is Conservation Technology?
Conservation Technology is the application of modern science, software and technology to environmental management challenges, aimed at protecting and preserving our natural world. As a rapidly growing field, it harnesses the latest innovations to tackle pressing conservation issues, making it critical for a sustainable future.
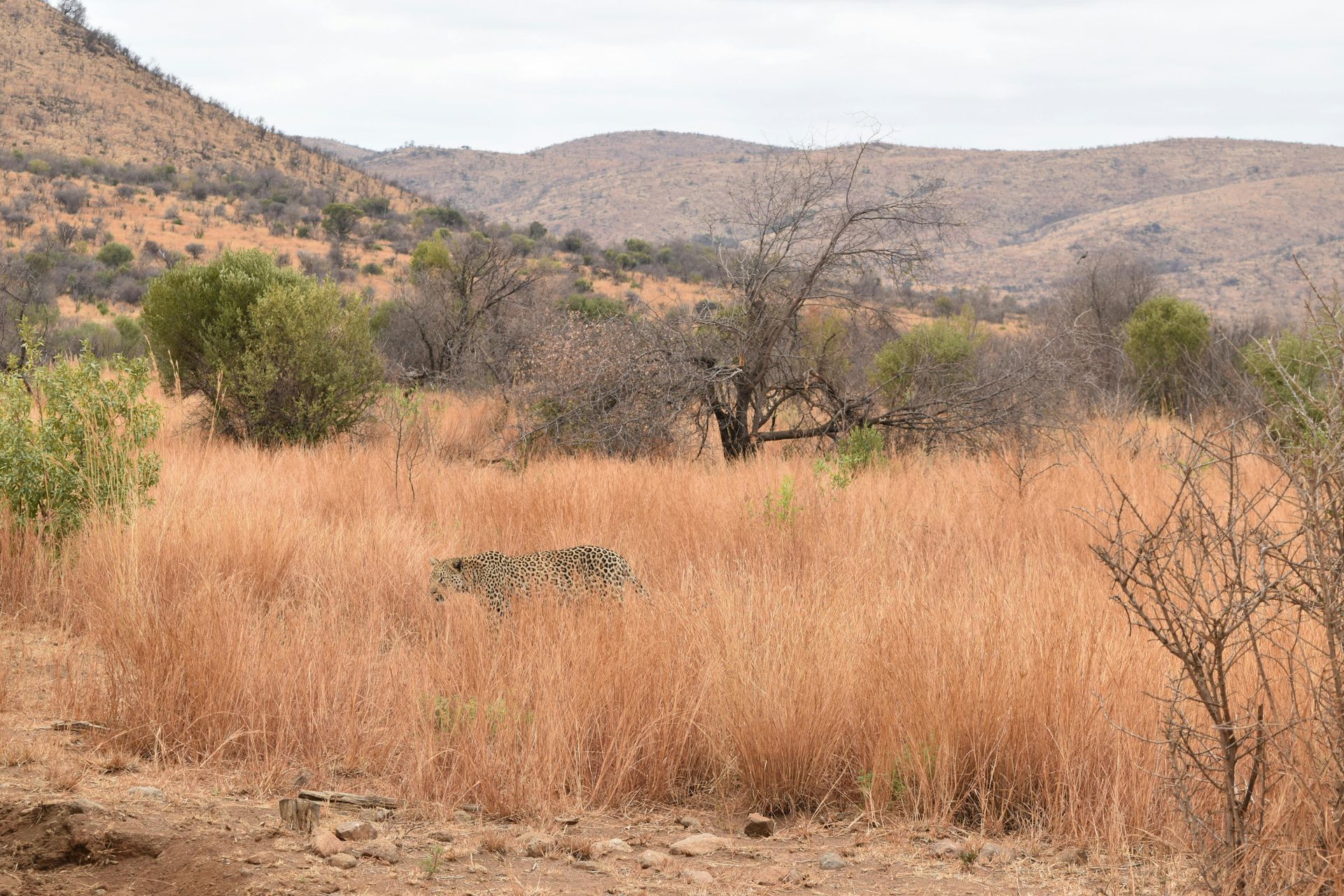
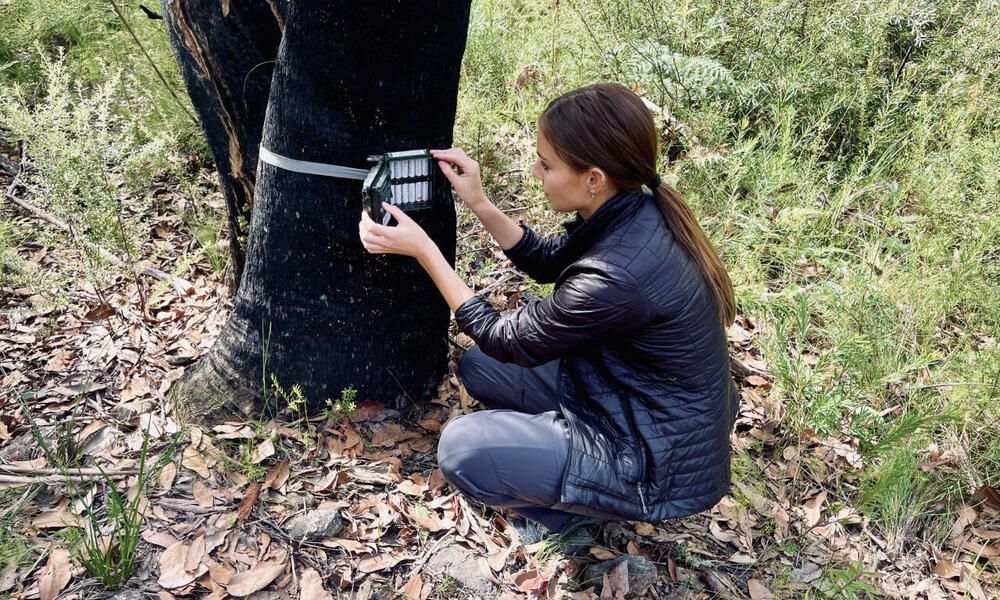
The Power of Camera Traps
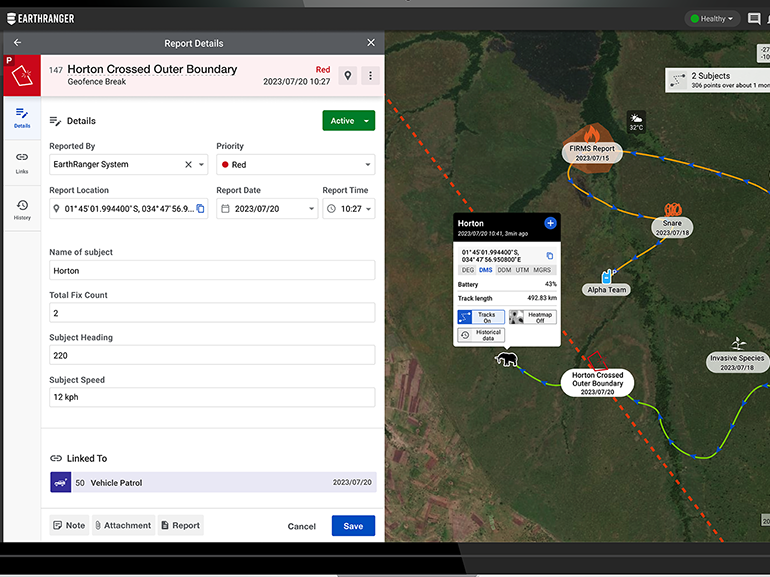
One of the most revolutionary tools in conservation technology is the camera trap. These devices, strategically placed in the wild, have become indispensable for monitoring elusive and rare species. Camera traps provide a non-invasive means of capturing detailed images and videos of wildlife, offering insights into animal behavior, population dynamics, and habitat use. Moreover, they are invaluable in the fight against poaching and other illegal activities, helping conservationists protect threatened species and their environments.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) & Remote Sensing
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing are pivotal in modern conservation efforts. GIS technology allows conservationists to visualize, analyze, and interpret geographical data, enabling informed decision-making about wildlife protection and habitat management. Remote sensing, which involves capturing high-resolution images from a distance, further enhances our ability to monitor landscapes, detect deforestation, and observe changes in wildlife populations. These technologies are crucial for understanding the broad spatial patterns that impact biodiversity and conservation.
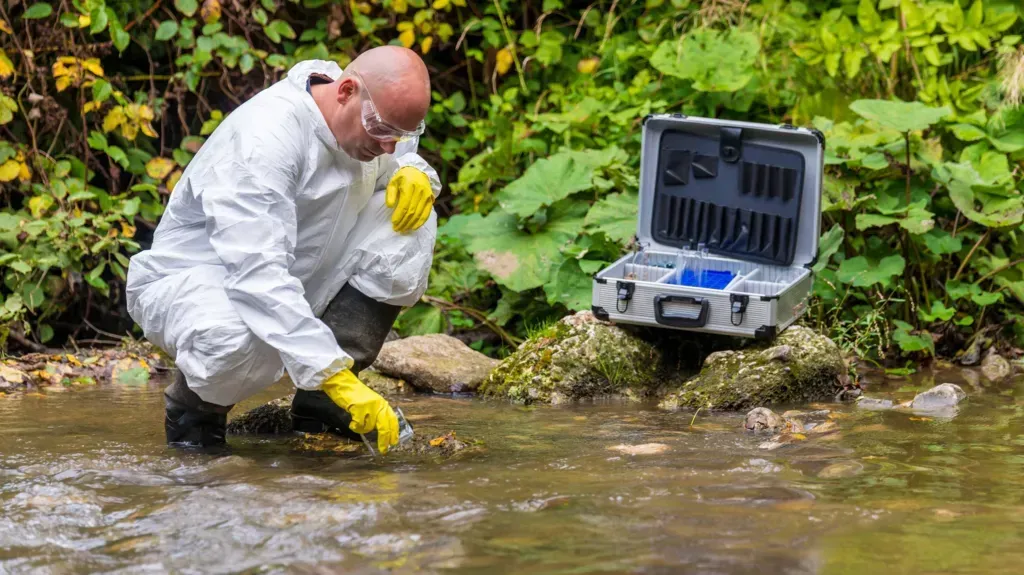
Environmental DNA & Genomics
The advent of environmental DNA (eDNA) and genomics has opened new frontiers in conservation. By analyzing DNA from soil or water samples, scientists can detect the presence of various species, including those that are difficult to observe directly. This technique provides a quick and comprehensive snapshot of an ecosystem's health and biodiversity, enabling conservationists to make data-driven decisions to protect endangered species and critical habitats.
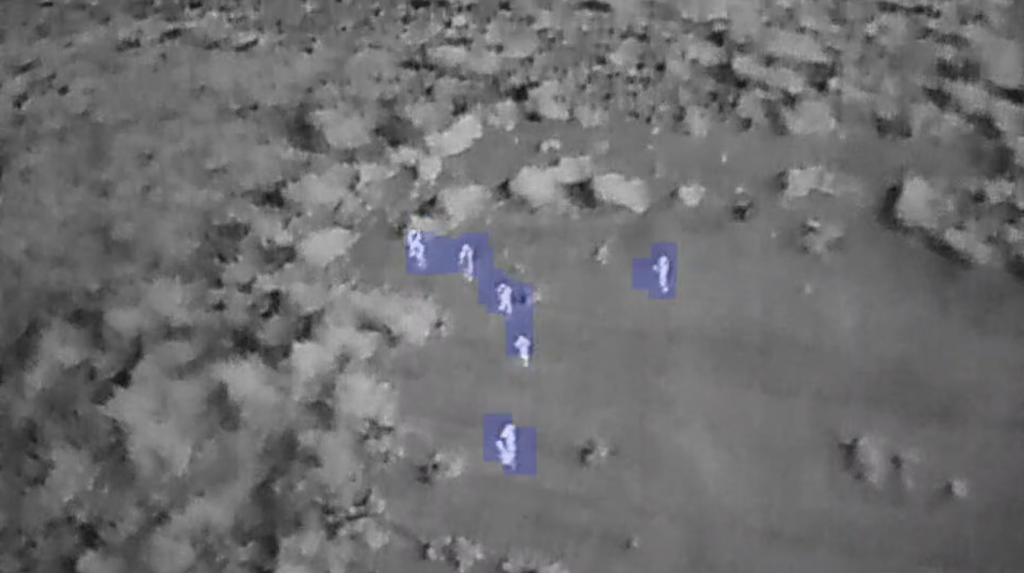
The Role of Drones in Conservation
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have become increasingly important in conservation technology. These devices can quickly and non-invasively gather high-resolution data on wildlife and habitats. Equipped with advanced sensors, drones can track animal movements, survey large and inaccessible areas, and even detect poachers in real-time. Thermal drones, which detect heat sources and convert them into digital images, are particularly useful in locating and monitoring wildlife that would otherwise be invisible to the naked eye.
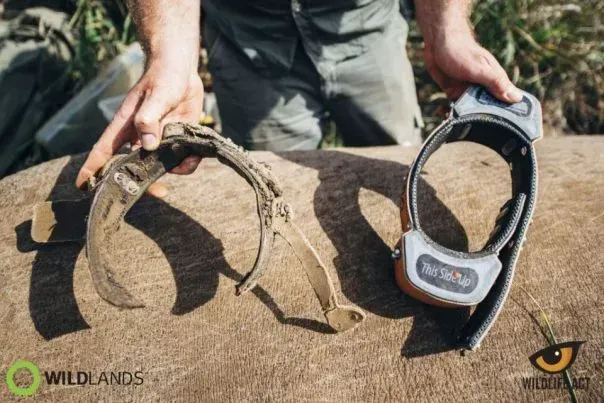
Biologging: Tagging & Tracking Wildlife
Biologging, which involves attaching electronic tags to animals, is another key component of conservation technology. These tags provide valuable data on the movements, behavior, and environmental interactions of wildlife. Real-time tracking of species, such as elephants or sea turtles, not only aids in their protection but also provides insights into the challenges they face from human activities, such as habitat destruction and illegal trafficking.
Acoustic Monitoring
Acoustic monitoring has advanced significantly, allowing for the long-term study of wildlife through sound. These devices capture the calls and songs of various species, helping researchers identify populations, track their movements, and assess the health of their habitats. Acoustic data is particularly useful in studying nocturnal or otherwise elusive animals, providing a fuller understanding of the ecosystem.
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are rapidly transforming conservation software. By automating the analysis of vast datasets, these tools can accelerate species identification, monitor wildlife in real-time, and even predict threats to endangered species. AI's ability to process and analyze complex information far exceeds human capabilities, making it an indispensable tool in the race to protect our planet's biodiversity.
Overcoming Barriers to Conservation Technology
Despite its potential, conservation technology faces several challenges. High costs, a lack of technical skills, and limited access to training can hinder the widespread adoption of these tools. Additionally, there is often competition for funding and difficulties in scaling and sustaining technological solutions. Overcoming these barriers requires collaboration across sectors, investment in capacity building, and the development of user-friendly, adaptable technologies.
Maximizing the Impact of Conservation Technology
To fully realize the potential of conservation technology, a collaborative approach is essential. Open and accessible solutions that are tailored to specific conservation needs, combined with global data sharing and local capacity building, will drive the effectiveness of these tools. Moreover, translating technological insights into actionable conservation strategies on the ground is crucial for achieving long-term success.
The Future of Conservation Technology
As technology continues to evolve, its role in conservation will only become more critical. From camera traps to drones, and from AI to eDNA, these tools are helping us protect our planet in ways that were once unimaginable. By embracing innovation and fostering collaboration, we can ensure that conservation technology remains a powerful force for good, safeguarding the natural world for generations to come.
Find Out More:
- WWF Camera Trapping
- Connected Conservation Foundation
- WildLabs.net
- Conservation Software
- AI In Conservation
- Nature Tech
Understanding the Difference: Conservation Technology vs. Sustainable, Environmental, and Green Technology
In discussions about technology's role in protecting the planet, terms like Sustainable Technology, Environmental Technology, Green Technology, and Conservation Technology are often used interchangeably. However, while these concepts are related, each plays a distinct role in addressing environmental challenges.
Sustainable Technology refers to innovations designed to meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. It emphasizes long-term resource management and minimizing environmental impact through practices like renewable energy production, sustainable agriculture, and energy-efficient manufacturing.
Environmental Technology encompasses a broad range of tools and techniques specifically aimed at reducing human impact on the environment. This includes pollution control technologies, waste management systems, and methods for reducing carbon emissions. It is primarily focused on mitigating the harmful effects of industrial activities on the natural world.
Green Technology is a subset of environmental technology that focuses on products and processes that are environmentally friendly. It includes advancements in renewable energy, electric vehicles, sustainable building materials, and more. The goal of green technology is to create solutions that contribute to a healthier planet.
Conservation Technology, on the other hand, is specifically geared towards preserving and protecting biodiversity, ecosystems, and natural habitats. While it shares a common goal with sustainable, environmental, and green technologies—namely, the protection and preservation of the natural world—conservation technology is distinct in its focus. It utilizes tools like drones, AI, and remote sensing to monitor wildlife, prevent poaching, and manage protected areas. Conservation technology is often employed in specific geographic areas like national parks and reserves and is crucial in efforts to combat illegal wildlife trade and habitat destruction.
In summary:
- Sustainable Technology is about long-term resource management and minimal environmental impact.
- Environmental Technology focuses on reducing human impact on the environment.
- Green Technology emphasizes environmentally friendly products and processes.
- Conservation Technology is dedicated to the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystems through specialized tools and techniques.
By understanding these differences, it becomes clear that while Conservation Technology intersects with Sustainable Technology, Environmental Technology, and Green Technology, it serves a unique and vital role in the broader effort to protect our planet.
Frameworks of Conservation Technology
Conservation Technology is revolutionizing the way we protect ecosystems and biodiversity. By integrating cutting-edge tools and methodologies, it enables more efficient and effective conservation efforts. In this section, we explore the frameworks that help guide the adoption of these technologies, offering professionals a structured approach to understanding their impact and value in the field. Delve into the core elements of Conservation Technology
Frequently Asked Questions
What is conservation technology?
Conservation technology refers to the application of advanced tools and methods in science and engineering to address environmental challenges, protect natural resources, and support biodiversity conservation. It involves using innovative solutions like drones, sensors, and AI to monitor ecosystems, combat illegal wildlife trade, and enhance sustainable practices in conservation efforts.
What is the role of technology in environmental conservation?
Technology plays a crucial role in environmental conservation by providing tools that enable more efficient monitoring, data collection, and analysis. It helps conservationists track endangered species, manage natural resources, and implement strategies that mitigate environmental threats. By enhancing accuracy and scalability, technology supports the preservation of ecosystems and the sustainable use of natural resources.
What can conservation, increased efficiency, and technology help manage?
Conservation, increased efficiency, and technology can help manage a wide range of environmental challenges, including wildlife protection, habitat restoration, water and energy conservation, and sustainable agricultural practices. These tools enable better resource management, reduce environmental impact, and promote sustainability in various sectors.
How do science and technology help in biodiversity conservation?
Science and technology help in biodiversity conservation by providing precise methods to study ecosystems, track species populations, and assess environmental changes. Technologies like genetic analysis, remote sensors, and geographic information systems (GIS) facilitate the understanding of complex ecosystems and support conservation strategies aimed at preserving biodiversity.
How does technology help in water conservation?
Technology helps in water conservation by offering tools like smart irrigation systems, water-efficient appliances, and real-time monitoring sensors. These technologies optimize water use, reduce waste, and ensure that water resources are managed sustainably, particularly in agriculture and urban settings.
How can technology transform conservation?
Technology can transform conservation by enabling more effective and scalable solutions for monitoring, protecting, and restoring natural environments. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, drones, and blockchain can revolutionize data collection, enforce environmental laws, and engage communities in conservation efforts, making conservation more efficient and impactful.
How can technology transform wildlife conservation?
Technology can transform wildlife conservation by providing advanced tools like camera traps, GPS tracking devices, and drones for monitoring wildlife populations and habitats. These technologies enable more accurate data collection, support anti-poaching efforts, and facilitate the creation of effective conservation strategies, ensuring the survival of endangered species.
Share this article
Quicklinks